So, you’re thinking about installing solar? Smart move. With rising electricity prices and growing climate awareness, more Indians are exploring solar systems. But here’s the big question — should you go on-grid or off-grid?
The answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. Whether you’re looking to save on your electricity bill or need reliable power in a rural location, understanding both systems is key.
Let’s break down everything you need to know to make an informed decision in 2025 — no jargon, just facts.
Understanding On-Grid Solar Systems
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
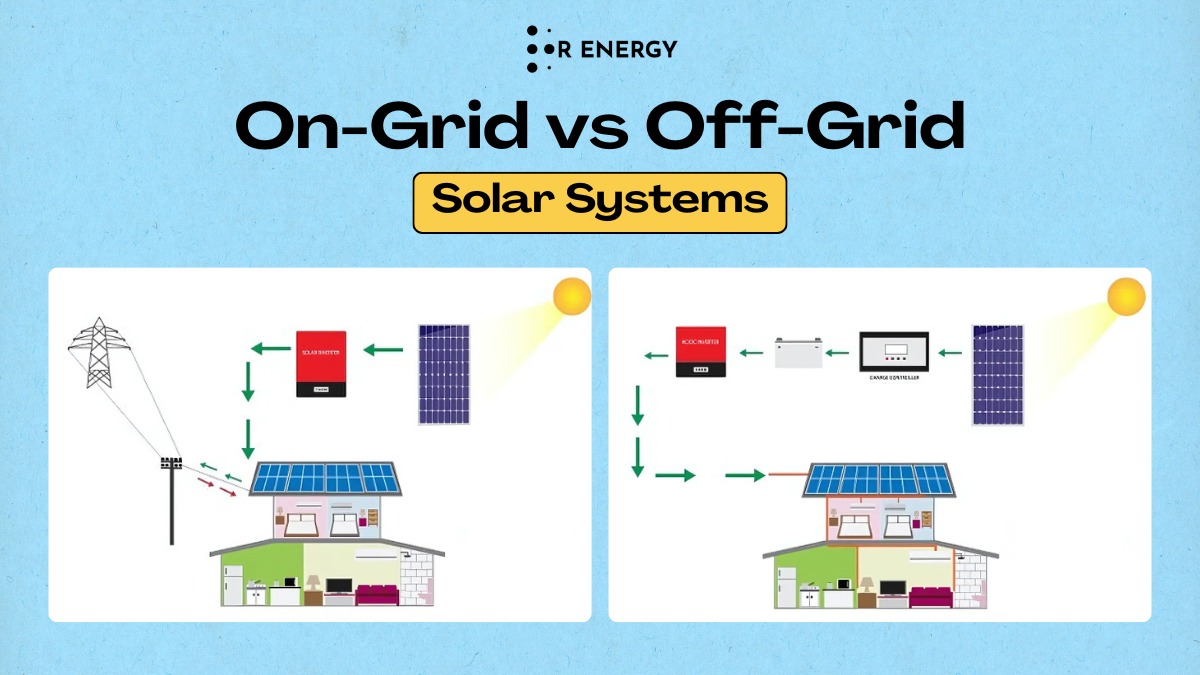
An on-grid or grid-tied solar system connects directly to the local utility grid. During the day, your solar panels generate power. If your home needs more, it draws from the grid. If you generate excess, it goes back to the grid.
Key Components
- Solar panels
- Inverter (converts DC to AC)
- Net meter
- No battery needed!
Benefits of On-Grid Systems
- Lower upfront cost since no battery is required
- Net metering allows you to earn credits for surplus power
- High efficiency in urban areas with stable grid supply
- Government subsidies available for residential homes
Drawbacks
- No power during blackouts unless combined with a battery
- Not suitable for remote or off-grid areas
Understanding Off-Grid Solar Systems
What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid system operates independently of any utility grid. It stores power in batteries for night-time or cloudy-day use.
Core Components
- Solar panels
- Inverter
- Charge controller
- Battery bank
Advantages
- 100% energy independence
- Ideal for remote villages or farms
- No reliance on the government or power companies
- Works even during blackouts
Challenges
- Higher installation cost due to batteries
- Battery maintenance and lifespan can be costly
- You must calculate your energy needs precisely to avoid shortages
On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar: Side-by-Side Comparison
1. Installation Cost
- On-grid: Lower, simpler setup.
- Off-grid: Higher due to battery storage.
2. Power Reliability
- On-grid: Depends on local grid reliability.
- Off-grid: Reliable if sized correctly, even during outages.
3. Energy Storage
- On-grid: No batteries needed.
- Off-grid: Batteries are essential.
4. Government Support
- On-grid systems benefit more from net metering and subsidies.
- Off-grid solutions have specific rural support schemes.
Which Solar System Is Best for You?
Go On-Grid If…
- You live in a city or town
- You want to reduce your electricity bills
- You prefer a low-maintenance system
Choose Off-Grid If…
- You’re in a rural or remote location
- You face frequent power cuts
- You want full energy independence
Consider Hybrid Systems
A hybrid system combines both — you stay connected to the grid but also store energy in batteries. It’s the best of both worlds if you can afford it.
Government Support in India (2025 Update)
Solar Subsidies
The Indian government, under MNRE, offers up to 40% subsidy for residential rooftop solar installations in 2025.
Net Metering Policy
Net metering allows homeowners to export surplus power back to the grid, reducing your monthly electricity bills significantly.
Support for Rural India
Special off-grid schemes are available for villages and remote regions under the DDUGJY (Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana).
🚀 Future Trends in Solar
Smart Solar with IoT
New inverters come with real-time monitoring apps and smart grid integration.
Better Battery Tech
Lithium-ion batteries are becoming cheaper, lighter, and longer-lasting.
Driving India’s Clean Energy Vision
India aims to generate 50% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, and solar will be a big player.
Conclusion
So, which is better?
If you live in a city and want affordability with grid support, go on-grid. If you live off-the-beaten-path or want full control, off-grid is the way. Evaluate your location, budget, and electricity needs — and you’ll land on the right choice.
Solar is no longer the future — it’s the present. Whether on-grid or off-grid, switching to solar is a step toward freedom, sustainability, and smart living.